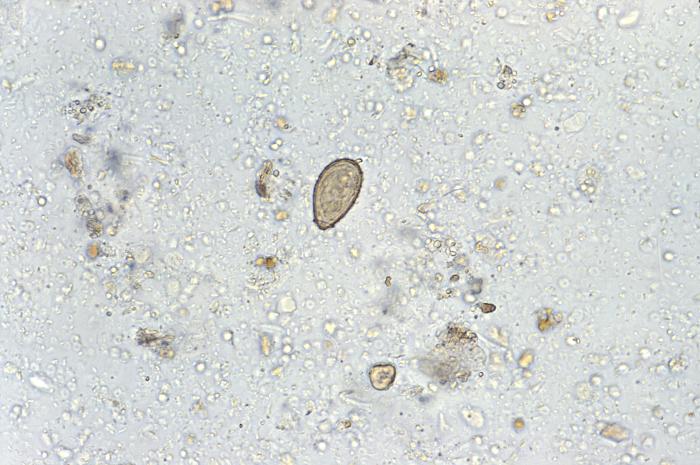
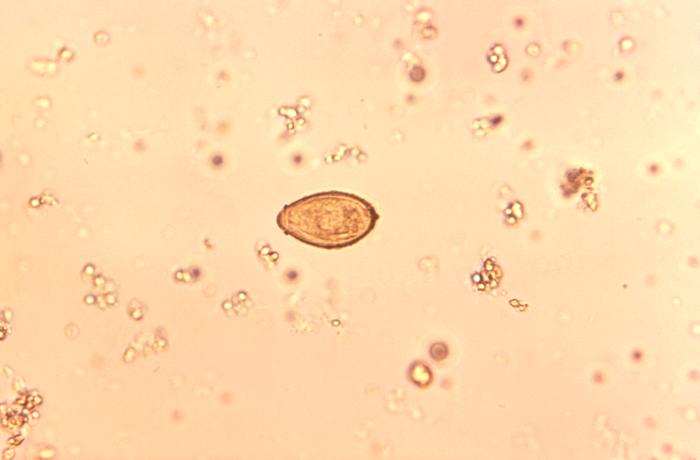
[1]
Hong ST,Fang Y, Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis, an update. Parasitology international. 2012 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 21741496]
[2]
Qian MB,Chen YD,Yan F, Time to tackle clonorchiasis in China. Infectious diseases of poverty. 2013 Feb 19;
[PubMed PMID: 23849773]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[3]
Kim TS,Pak JH,Kim JB,Bahk YY, Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: a brief review. BMB reports. 2016 Nov;
[PubMed PMID: 27418285]
[4]
Yoshida Y, Clonorchiasis--a historical review of contributions of Japanese parasitologists. Parasitology international. 2012 Mar;
[PubMed PMID: 21749930]
[5]
Control of foodborne trematode infections. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organization technical report series. 1995
[PubMed PMID: 7740791]
[6]
Qian MB,Utzinger J,Keiser J,Zhou XN, Clonorchiasis. Lancet (London, England). 2016 Feb 20
[PubMed PMID: 26299184]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[7]
Fürst T,Keiser J,Utzinger J, Global burden of human food-borne trematodiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet. Infectious diseases. 2012 Mar;
[PubMed PMID: 22108757]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[8]
Qian MB,Chen YD,Liang S,Yang GJ,Zhou XN, The global epidemiology of clonorchiasis and its relation with cholangiocarcinoma. Infectious diseases of poverty. 2012 Oct 25;
[PubMed PMID: 23849183]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[9]
Sripa B, Concerted action is needed to tackle liver fluke infections in Asia. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2008 May 28
[PubMed PMID: 18509525]
[10]
Fang YY,Chen YD,Li XM,Wu J,Zhang QM,Ruan CW, [Current prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infection in endemic areas of China]. Zhongguo ji sheng chong xue yu ji sheng chong bing za zhi = Chinese journal of parasitology
[PubMed PMID: 24812810]
[11]
Wang KX,Zhang RB,Cui YB,Tian Y,Cai R,Li CP, Clinical and epidemiological features of patients with clonorchiasis. World journal of gastroenterology. 2004 Feb 1
[PubMed PMID: 14760777]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[12]
Qian MB,Zhuang SF,Zhu SQ,Deng XM,Li ZX,Zhou XN, Epidemiology and determinants of clonorchiasis in school children in southeastern China. Acta tropica. 2021 Apr;
[PubMed PMID: 33188749]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[13]
Qian MB,Chen YD,Fang YY,Tan T,Zhu TJ,Zhou CH,Wang GF,Xu LQ,Zhou XN, Epidemiological profile of Clonorchis sinensis infection in one community, Guangdong, People's Republic of China. Parasites
[PubMed PMID: 23816055]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[15]
Bouvard V,Baan R,Straif K,Grosse Y,Secretan B,El Ghissassi F,Benbrahim-Tallaa L,Guha N,Freeman C,Galichet L,Cogliano V,WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group., A review of human carcinogens--Part B: biological agents. The Lancet. Oncology. 2009 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 19350698]
[16]
Zheng M,Hu K,Liu W,Hu X,Hu F,Huang L,Wang P,Hu Y,Huang Y,Li W,Liang C,Yin X,He Q,Yu X, Proteomic analysis of excretory secretory products from Clonorchis sinensis adult worms: molecular characterization and serological reactivity of a excretory-secretory antigen-fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Parasitology research. 2011 Sep;
[PubMed PMID: 21424807]
[18]
Kim JH,Choi MH,Bae YM,Oh JK,Lim MK,Hong ST, Correlation between discharged worms and fecal egg counts in human clonorchiasis. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2011 Oct;
[PubMed PMID: 21991401]
[19]
Lun ZR,Gasser RB,Lai DH,Li AX,Zhu XQ,Yu XB,Fang YY, Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. The Lancet. Infectious diseases. 2005 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 15620559]
[20]
Qiao T,Ma RH,Luo ZL,Yang LQ,Luo XB,Zheng PM, Clonorcis sinensis eggs are associated with calcium carbonate gallbladder stones. Acta tropica. 2014 Oct;
[PubMed PMID: 24945791]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[21]
Choi D,Lim JH,Lee KT,Lee JK,Choi SH,Heo JS,Choi DW,Jang KT,Lee NY,Kim S,Hong ST, Gallstones and Clonorchis sinensis infection: a hospital-based case-control study in Korea. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2008 Aug;
[PubMed PMID: 18070015]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[23]
Papachristou GI,Schoedel KE,Ramanathan R,Rabinovitz M, Clonorchis sinensis-associated cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Digestive diseases and sciences. 2005 Nov;
[PubMed PMID: 16240232]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[24]
Hong ST,Choi MH,Kim CH,Chung BS,Ji Z, The Kato-Katz method is reliable for diagnosis of Clonorchis sinensis infection. Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease. 2003 Sep;
[PubMed PMID: 12967748]
[25]
Joo KR,Bang SJ, A bile based study of Clonorchis sinensis infections in patients with biliary tract diseases in Ulsan, Korea. Yonsei medical journal. 2005 Dec 31;
[PubMed PMID: 16385655]
[26]
Qian MB,Yap P,Yang YC,Liang H,Jiang ZH,Li W,Utzinger J,Zhou XN,Keiser J, Accuracy of the Kato-Katz method and formalin-ether concentration technique for the diagnosis of Clonorchis sinensis, and implication for assessing drug efficacy. Parasites
[PubMed PMID: 24499644]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[27]
Kim EM,Verweij JJ,Jalili A,van Lieshout L,Choi MH,Bae YM,Lim MK,Hong ST, Detection of Clonorchis sinensis in stool samples using real-time PCR. Annals of tropical medicine and parasitology. 2009 Sep;
[PubMed PMID: 19695156]
[28]
Hong ST,Yoon K,Lee M,Seo M,Choi MH,Sim JS,Choi BI,Yun CK,Lee SH, Control of clonorchiasis by repeated praziquantel treatment and low diagnostic efficacy of sonography. The Korean journal of parasitology. 1998 Dec;
[PubMed PMID: 9868890]
[30]
Choi D,Hong ST,Lim JH,Cho SY,Rim HJ,Ji Z,Yuan R,Wang S, Sonographic findings of active Clonorchis sinensis infection. Journal of clinical ultrasound : JCU. 2004 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 14705173]
[31]
Jeong YY,Kang HK,Kim JW,Yoon W,Chung TW,Ko SW, MR imaging findings of clonorchiasis. Korean journal of radiology. 2004 Jan-Mar
[PubMed PMID: 15064556]
[32]
Xu LL,Jiang B,Duan JH,Zhuang SF,Liu YC,Zhu SQ,Zhang LP,Zhang HB,Xiao SH,Zhou XN, Efficacy and safety of praziquantel, tribendimidine and mebendazole in patients with co-infection of Clonorchis sinensis and other helminths. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2014 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 25122121]
[33]
Keiser J,Utzinger J, The drugs we have and the drugs we need against major helminth infections. Advances in parasitology. 2010
[PubMed PMID: 20627144]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[34]
Lee SH, Large scale treatment of Clonorchis sinensis infections with praziquantel under field conditions. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 1984;
[PubMed PMID: 6542401]
[35]
Choi MH,Park SK,Li Z,Ji Z,Yu G,Feng Z,Xu L,Cho SY,Rim HJ,Lee SH,Hong ST, Effect of control strategies on prevalence, incidence and re-infection of clonorchiasis in endemic areas of China. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2010 Feb 16;
[PubMed PMID: 20169061]
[36]
Liu YH,Wang XG,Gao P,Qian MX, Experimental and clinical trial of albendazole in the treatment of Clonorchiasis sinensis. Chinese medical journal. 1991 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 1879192]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[37]
Qian MB,Yap P,Yang YC,Liang H,Jiang ZH,Li W,Tan YG,Zhou H,Utzinger J,Zhou XN,Keiser J, Efficacy and safety of tribendimidine against Clonorchis sinensis. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2013 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 23223597]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[38]
Lee SH,Hong ST,Kim CS,Sohn WM,Chai JY,Lee YS, Histopathological changes of the liver after praziquantel treatment in Clonorchis sinensis infected rabbits. Kisaengch'unghak chapchi. The Korean journal of parasitology. 1987 Dec
[PubMed PMID: 12886061]
[39]
Zhang GW,Lin JH,Qian JP,Zhou J, Identification of risk and prognostic factors for patients with clonorchiasis-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Annals of surgical oncology. 2014 Oct;
[PubMed PMID: 24781504]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[40]
Tan SK,Qiu XQ,Yu HP,Zeng XY,Zhao YN,Hu L, [Evaluation of the risk of clonorchiasis inducing primary hepatocellular carcinoma]. Zhonghua gan zang bing za zhi = Zhonghua ganzangbing zazhi = Chinese journal of hepatology. 2008 Feb;
[PubMed PMID: 18304427]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[41]
Choi BI,Han JK,Hong ST,Lee KH, Clonorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma: etiologic relationship and imaging diagnosis. Clinical microbiology reviews. 2004 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 15258092]
[42]
Choi D,Lim JH,Lee KT,Lee JK,Choi SH,Heo JS,Jang KT,Lee NY,Kim S,Hong ST, Cholangiocarcinoma and Clonorchis sinensis infection: a case-control study in Korea. Journal of hepatology. 2006 Jun
[PubMed PMID: 16480786]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[43]
Tang ZL,Huang Y,Yu XB, Current status and perspectives of Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, omics, prevention and control. Infectious diseases of poverty. 2016 Jul 6
[PubMed PMID: 27384714]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence