Continuing Education Activity
Diverticulitis has increased in incidence over the past few decades and represents a significant healthcare burden in western countries. In the United States, acute diverticulitis is associated with nearly 200,000 hospital admissions and 2.2 billion dollars in healthcare costs per year. Although the prevalence of the disease increases with age, younger adults may also develop the diverticular disease. The management of colonic diverticulitis has changed significantly in recent years. The decision to perform elective sigmoid colectomy in patients that recover from uncomplicated diverticulitis is controversial and requires case-by-case consideration. Surgical treatment is the recommendation in cases of complicated diverticulitis. This activity reviews the epidemiology, presentation, and treatment of diverticulitis and highlights the interprofessional team's role in caring for affected patients.
Objectives:
- Describe the pathophysiology of diverticulitis.
- Outline the differences between complicated versus uncomplicated diverticulitis.
- Review the indications for medical versus surgical management of diverticulitis.
- Summarize the importance of collaboration and intradisciplinary teamwork for providing optimal care to patients with diverticulitis.
Introduction
Diverticulitis has increased in incidence over the past few decades, becoming a major healthcare burden for Western countries.[1] In the United States, acute diverticulitis results in nearly 200,000 hospital admissions and $2.2 billion in health care costs per year.[2] Although the prevalence of the disease increases with age, younger adults may also develop the diverticular disease. In fact, for some time, it was thought that younger and male patients were more likely to experience a more aggressive form of diverticulitis with an increased complication rate and higher recurrence.[3]
However, recent studies have challenged this concept. Environmental and genetic risk factors result in diverticular disease development, although good quality evidence for many of these factors remains insufficient. Most cases of diverticulitis undergo successful management in the outpatient setting with oral antibiotics and temporary dietary restrictions. The decision to perform elective sigmoid colectomy in patients that recover from uncomplicated diverticulitis is controversial and requires case-by-case consideration. Surgical treatment is the recommendation in cases of complicated diverticulitis.
Etiology
The diverticular disease starts with an out-pouching of the mucosa of the colonic wall. Inflammation at each mucosal out-pouching contributes to diverticulitis. The presumed mechanism of diverticulitis is an overgrowth of bacteria due to obstruction of the diverticular base by feces with micro-perforations. This theory has been challenged in recent years as some studies demonstrate that the resolution of uncomplicated diverticulitis may occur without antibiotics in selected cases.[4]
Epidemiology
Diverticulosis of the colon is common in western countries and increases with age. Over 50% of individuals over the age of sixty have diverticulosis, and the incidence rises to 70% after eighty years of age.[5] Despite the significant prevalence of diverticulosis in the population, only 4% of individuals will develop diverticulitis in their lifetime.[6] The distribution of the colonic diverticula varies depending on population demographics. In Western countries, diverticula are most common in the sigmoid colon, with a rate of 65%.[1] The right colon is more commonly involved in Asian populations. This difference was once attributed to daily dietary fiber, but epidemiologic studies have refuted this concept. These studies have analyzed Asian populations after relocation and changes in dietary habits, but there is no proof yet of any change in the diverticular pattern.[7] Although environmental factors play a significant role in diverticulosis development, studies on identical twins have identified a strong genetic predisposition.[8]
Multiple environmental risk factors have been postulated in the development of diverticular disease; however, many remain controversial. A 1970 study hypothesized that a diet high in fiber was protective against diverticular disease, but the evidence is conflicting.[9] For patients with a history of diverticulitis, The American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) and the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS) recommend a diet high in fiber. In this setting, increasing dietary fiber correlates with reducing the development of recurrent episodes of acute uncomplicated and complicated diverticulitis.[10]
In the past, patients with diverticular disease were discouraged from eating nuts, seeds, and popcorn, but a recent study determined that these foods do not increase the risk of developing diverticulitis.[11] Red meat, particularly beef and lamb, has been associated with an increased risk of diverticulitis hospitalization. Obesity, smoking, and alcohol use are also associated with a higher incidence of diverticular disease.[12] Medications, including NSAIDs, aminosalicylates (ASA), and acetaminophen, seem to increase the risk of developing complicated diverticulitis. Current corticosteroid use doubles the risk of developing perforated diverticulitis.[13]
There are also postulates regarding protective factors. Vigorous exercise, such as running, has shown a risk reduction of developing complicated diverticulitis by 25%. Light activity, such as walking, is less effective.[14] Statin medications appear to reduce the risk of perforated diverticulitis.[13] Maintaining a normal weight and eliminating smoking also decreases the risk of diverticular disease.
Pathophysiology
Despite the high prevalence of diverticulosis, the pathophysiology of the disease is not well understood. A colonic diverticulum is an out-pouching of the colonic mucosa through the weakest point in the colonic lumen, where the vasa recta penetrate the colonic wall to supply blood to the submucosa and mucosa. Patients with diverticulosis have increased intraluminal pressures during peristalsis.[4] High colonic intraluminal pressure associated with constipation and straining during defecation was once thought to be the initiating factor resulting in mucosal herniation through the colonic wall, but this theory is currently under question.[8]
History and Physical
Most patients with diverticulosis are asymptomatic, and the presence of diverticula is commonly identified incidentally during colonoscopy or radiologic studies. Patients with acute diverticulitis may present with fever, left lower quadrant pain, and change in bowel habits. Left lower abdominal pain is the most common presenting feature in 70% of patients. The character of pain is mainly described as crampy and may be associated with a change in bowel habits. Consequently, the presentation of diverticulitis may be confused with irritable bowel syndrome. Other symptoms of diverticulitis include nausea, vomiting, constipation, flatulence, and bloating. Acute presentation of diverticulitis may also be because of a complication, such as colonic abscess, intestinal perforation, and fistula formation.
Laboratory findings include leukocytosis and possibly elevated inflammatory markers.[15] Those patients with complicated diverticulitis may present with signs of sepsis and physical findings consistent with peritonitis. Physical findings may include abdominal tenderness, abdominal distension, a tender mass in the abdomen, absent bowel sounds, and findings related to fistula formation. The presence of fecaluria and pneumaturia must alert the clinician to the possibility of a colovesical fistula.
Evaluation
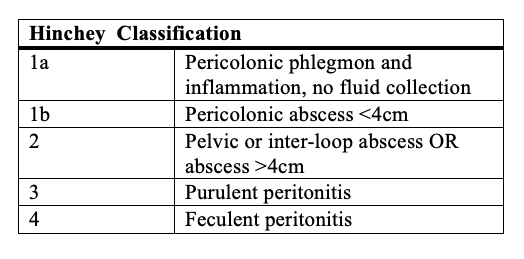
When the history, physical exam, and laboratory findings are consistent with the diagnosis of acute diverticulitis, confirmatory imaging studies are the next step. Different imaging modalities, including ultrasound and barium enema, may be used to diagnose diverticular disease. However, a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast is the preferred modality. Its diagnostic accuracy is high, with a sensitivity of 98%.[16] assessment of renal function before the administration of intravenous contrast is imperative. Findings of colonic wall thickening and fat stranding are typical for diverticulitis. Signs of complicated disease, including fistula formation, abscesses, and intra-abdominal free air, are easily identifiable with scans.[17] The Hinchey classification system is useful in determining the severity of disease and in allocating patients to different treatment algorithms.
Generally speaking, patients with Hinchey 1a and 1b diverticulitis are successfully manageable by non-surgical means. Patients with Hinchey 2 diverticulitis may require placement of a percutaneous drain followed by elective sigmoid colectomy. However, patients with Hinchey 3 and 4 require urgent surgical intervention.
A urinalysis may reveal red or white blood cells, prompting suspicion of a colovesical fistula. In females of childbearing age who present with abdominal pain, a pregnancy test must be carried out to rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment / Management
The medical management of acute non-complicated diverticulitis includes oral or intravenous antibiotics, pain control, hydration, and restricted oral intake. Medical management of diverticulitis with antibiotics remains the standard of care. However, antibiotic choice, duration of treatment, and route of administration remain controversial.[18] Most cases of uncomplicated diverticulitis are successfully treatable in the outpatient setting. Oral antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin and metronidazole or amoxicillin-clavulanate, are prescribed for 7 to 10 days with recommendations to minimize oral intake until the pain has resolved.[15]
Patients who are febrile, immunosuppressed, unable to stay hydrated, or those with multiple medical comorbidities require admission to the hospital for treatment with parenteral antibiotics. As symptoms improve, the diet is advanced, and patients are started on oral antibiotics. Any patient failing to improve on parenteral antibiotics or deteriorates during therapy should undergo repeat evaluation with CT imaging to rule out evolving complications.[15]
After acute episode resolution of diverticulitis, a colonoscopy is recommended 6 to 8 weeks later, particularly if the patient has not had a colonoscopy in the past 2 to 3 years.[15]
Historically, elective sigmoid colectomy used to be performed after the second bout of uncomplicated diverticulitis. However, more recent evidence has disproved the benefit of this approach. Firstly, the recurrence rate of uncomplicated diverticulitis is lower than previously estimated, ranging from 13 to 23%. Secondly, the incidence of complicated recurrent episodes that may require a stoma is also low, at approximately 6%. Therefore, current recommendations emphasize that selection criteria for elective surgery should be individualized according to the number, severity, and frequency of diverticulitis episodes, persistent symptomatology after an episode of diverticulitis, and the immunologic status of the patient. These criteria merit consideration in terms of the patient’s age, comorbidities, and social history. Finally, routine sigmoid colectomy in patients younger than 50 is no longer the recommended therapeutic path.[10] Younger patients should receive the same treatment as their older counterparts.
Regardless of the indication and technique used (open, laparoscopic, or robotic) when performing an elective sigmoid colectomy for diverticulitis, it requires removing the entire sigmoid colon, the proximal and distal anastomotic sites must appear healthy and well-perfused, and the anastomosis performed without tension.
Approximately 1% of patients with an acute episode of diverticulitis will require surgical intervention during that episode.[19] Patients presenting with signs of peritonitis are candidates for emergent surgery. When intraoperative findings confirm perforated diverticulitis, the traditional operation is a Hartmann procedure, which includes resection of the sigmoid colon, preservation of the rectum in the form of a rectal pouch, and creation of an end colostomy. This procedure eliminates the risk of an anastomotic leak, and patients are considered for colostomy reversal in 3 to 6 months. However, due to old age and associated comorbidities, nearly 30% of patients undergoing a Hartmann procedure never have colostomy reversal.[15]
A second option for patients with Hinchey 3 and 4 diseases is a primary colorectal anastomosis with a proximal diverting ileostomy. Initial retrospective evaluation of this surgical modality shows a decreased overall mortality after performing a primary anastomosis. However, randomized controlled studies comparing a Hartmann procedure to the primary anastomosis with proximal diversion are not yet available.[20] An old approach, no longer considered in the surgical management of complicated diverticulitis, consisted of leaving the inflamed or perforated sigmoid colon in situ and placing a proximal stoma with the plan of second and then third-stage procedures.
Acute colonic diverticulitis should be managed in a stepwise manner as follows:
- If the patient meets any of the following criteria, they should be admitted for inpatient management.[21]
- Presence of evidence suggestive of complicated diverticulitis, including:
- Frank perforation
- Abscess formation in a symptomatic patient
- Bowel obstruction
- Complicated colonic diverticula with a fistula formation
- Evidence of sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) suggestive by equal or more than two of the following indexes;
- Temperature of greater than 38 C or less than 36
- Heart rate of greater than 90 beats per minute
- Respiratory rate of greater than 20 breaths per minute
- WBC of greater than 12,000 cells/mm^3 or less than 4,000 cells/mm^3
- C-reactive protein (CRP) level of greater than 15 mg/dl[21]
- Physical examination suggestive of diffuse, non-localized peritonitis
- Evidence of micro-perforations in the imaging measures, including the presence of few extramural colonic micro-bubbles
- Advanced age; older than 70
- Remarkable comorbidities, including but not limited to:
- Diabetes mellitus with end-organ damage (e.g., presence of retinopathy, microangiopathy, and nephropathy)
- Recent cardiovascular event, including acute myocardial infarction
- Immunocompromised status
- Oral intake intolerance
Inpatient management should be initiated with intravenous antibiotics, hydration, pain control with intravenous medications, and complete bowel rest. However, dietary limitations to a liquid diet have also been investigated in some centers.[21]
In patients with signs and symptoms of acute colonic diverticulitis who do not meet the criteria to be admitted for inpatient management, outpatient treatment with pain control and a liquid diet should e triggered. However, the response to the conservative outpatient treatment should be re-evaluated within the first 72 hours. Those without improvement evidence should be admitted for inpatient management. On the contrary, the responders to conservative management should be approached with diet advancement and clinical reassessment weekly. If all the symptoms are resolved within six weeks after the index episode, performing an elective colonoscopy should be scheduled.[21][22]
It should be noted that even in patients with normal colonoscopy, surgical referral for further evaluation should be considered in the following circumstances; 1. immunocompromised patients, and 2. complicated episode of diverticulitis.[22] Otherwise, a high-fiber diet is recommended.
- If the patient does not meet any of the mentioned criteria, outpatient treatment with pain control and a liquid diet should be initiated. Still, clinical improvement should be evaluated in two or three days.
- In the absence of clinical improvement within three days, inpatient management should be initiated with intravenous antibiotics, hydration, pain control with intravenous medications, and complete bowel rest. However, dietary limitations to a liquid diet have also been investigated in some centers.[21]
- During inpatient management, frank perforation, obstruction, or fistula formation should be evaluated. In the presence of any of these complications, surgical referral should be considered.
- In the absence of the mentioned complications, the next step is to evaluate the presence of a drainable abscess equal to or greater than 4 cm in size, which should be drained percutaneously.
- If the abscess is less than 4 cm, the clinical improvement within the first three days should be examined.
Differential Diagnosis
Diverticulitis can occur anywhere in the colon; hence, the presentation may vary according to the site involved. For instance, diverticulitis in the right colon may present similarly to acute appendicitis. Similarly, diverticula in the transverse colon may appear as peptic ulcer disease, pancreatitis, or cholecystitis. Therefore the list of differential diagnoses is extensive as follows:
- Acute gastritis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Acute appendicitis
- Acute cholecystitis
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Cholangitis
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Constipation
- Irritable bowel disease
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Ovarian cyst
- Ectopic pregnancy
Pertinent Studies and Ongoing Trials
Recent studies have demonstrated the resolution of uncomplicated diverticulitis without the use of antibiotics in very well-selected patients. Patients with peritonitis, perforation, signs of sepsis, and hemodynamic instability were excluded. Although some patients did develop perforations or abscesses, the risk was considered low. There was no difference in primary outcomes between the group treated with antibiotics and those without antibiotic therapy.[18] The evidence for this unique treatment approach is preliminary, and further study is needed.
Traditionally, patients with generalized peritonitis from perforated diverticulitis undergo a Hartman procedure or primary anastomosis with a proximal diverting stoma. Researchers have studied laparoscopic peritoneal lavage as an alternative to the standard surgical treatment of perforated diverticulitis.[23] Other studies have not duplicated the initial results, so this treatment remains controversial.
Prognosis
The prognosis of the patients depends on the severity of the illness and the presence of complications. Immunocompromised patients have higher morbidity and mortality as a result of sigmoid diverticulitis.[24]
After the first incident of acute diverticulitis, the five-year recurrence rate is approximately 20%.[25] Several studies have demonstrated the significant link between increased BMI and the risk of developing diverticulitis.[26]
Complications
Many complications can occur in a patient with diverticulitis, which can be more severe in certain cases, such as in immunocompromised patients. For instance, those infected with HIV or those on immunosuppressants are more likely to develop perforation.[27] The following are the possible complications of diverticulitis:
- Abscess formation (commonest)
- Intestinal perforation
- Intestinal fistula
- Intestinal obstruction
- Generalized peritonitis
- Stricture disease
- Sepsis
Consultations
Interprofessional teams must deliver the present management of diverticulitis in the context of the most recent scientific evidence. These teams can include gastroenterologists, internists, general surgeons, colostomy care nurses, gastroenterology specialty-trained nurses, and pharmacists, working collaboratively to bring about optimal patient care and outcomes.
Deterrence and Patient Education
To help prevent a recurrence of their condition, patients are advised to consume a high-fiber diet, drink 6 to 8 glasses of water daily, exercise, monitor any changes in their bowel movements, and use a stool softener if they become constipated.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The incidence of diverticulitis continues to increase in all age groups, placing a substantial burden on the healthcare system. The interprofessional healthcare team, consisting of primary care physicians, NPs, PAs, gastroenterologists, nurses, pharmacists, and dietitians, must educate the public and patients that obesity, inactivity, and a poor diet contribute significantly to epidemiologic factors.
Pharmacists will perform medication reconciliation when drug therapy is part of the treatment; they can also counsel patients on their medications, assist with dosing, and report any concerns to the prescribing clinician. Nurses will coordinate activities between the various clinicians and specialists on the case and also offer patients counsel on their condition. They are also responsible for assisting during surgery and monitoring patients post-procedure.
A positive paradigm change in diverticulitis treatment has resulted in the widespread use of outpatient management for non-complicated diverticulitis. However, many patients with a history of non-complicated diverticulitis are improperly managed empirically with antibiotics every time they call their clinician’s office with abdominal pain. This misuse of antibiotics must be corrected. For patients undergoing surgery, a colostomy nurse should educate the patient on the care of the stoma. All care team members must utilize meticulous record-keeping so that every caregiver on the case can access the same updated patient information.
Better and more sophisticated imaging modalities have allowed us to accurately classify disease severity and allocate different patients to more effective treatment algorithms.
The current emphasis on individualizing the need for elective sigmoid colectomy after resolving non-complicated diverticulitis will result in fewer unnecessary operations and better outcomes. [Level 5]