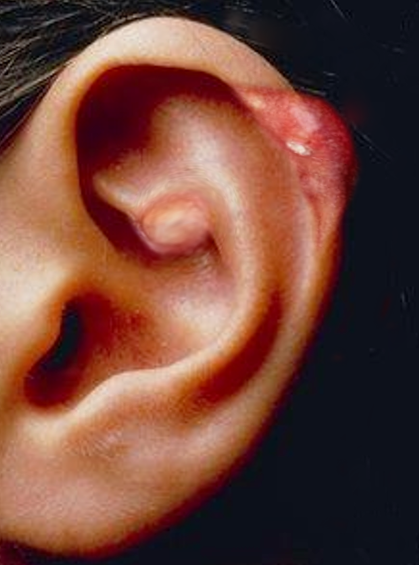
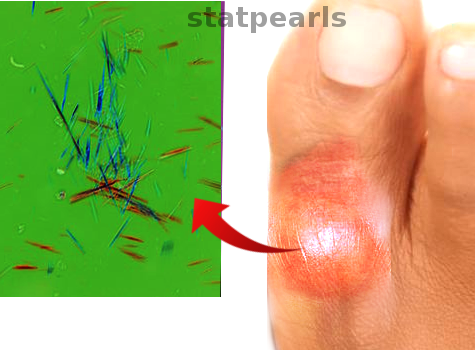
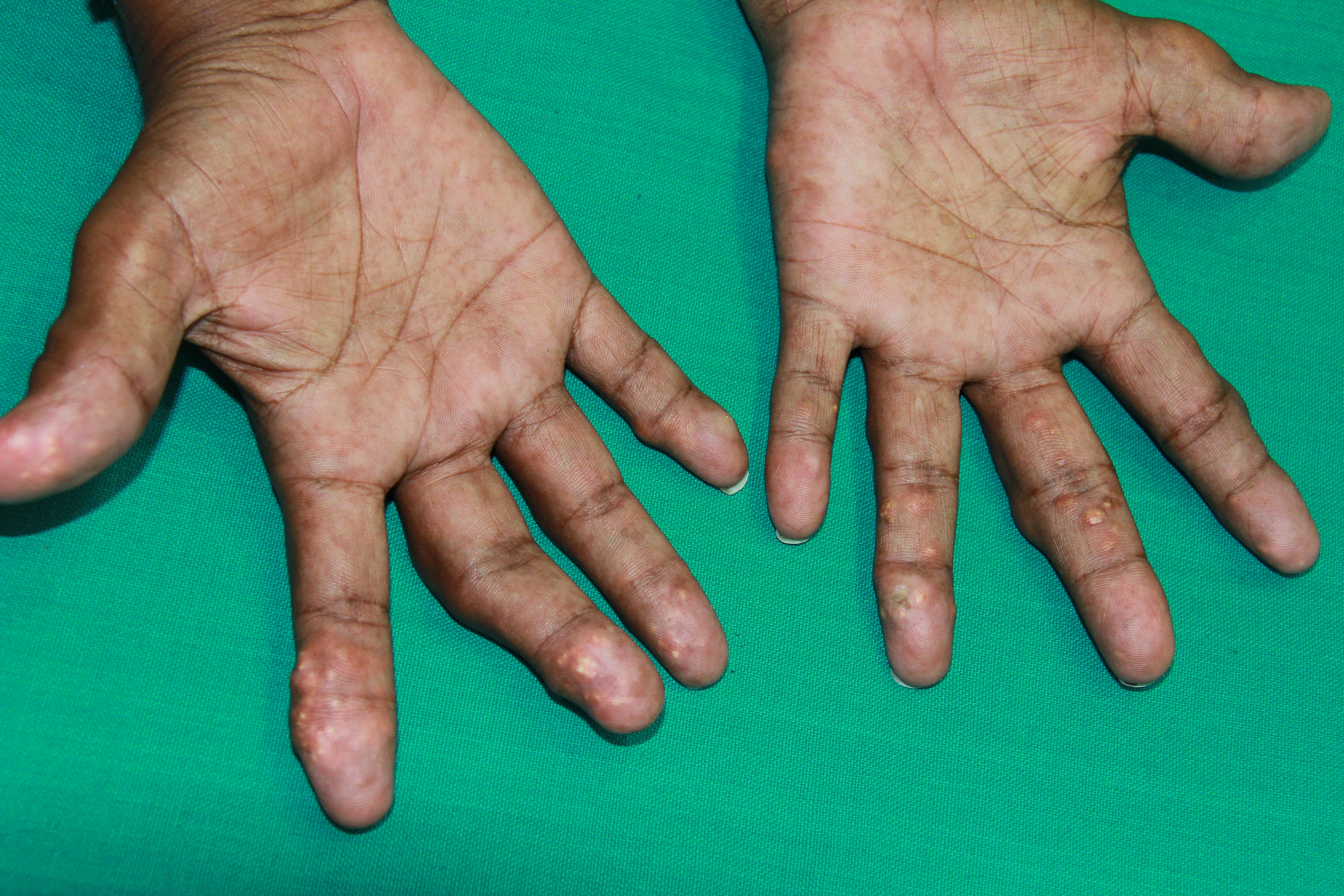
[1]
Neogi T. Gout. Annals of internal medicine. 2016 Jul 5:165(1):ITC1-ITC16. doi: 10.7326/AITC201607050. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 27380294]
[2]
Dalbeth N, Merriman TR, Stamp LK. Gout. Lancet (London, England). 2016 Oct 22:388(10055):2039-2052. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00346-9. Epub 2016 Apr 21
[PubMed PMID: 27112094]
[3]
Richette P, Bardin T. Gout. Lancet (London, England). 2010 Jan 23:375(9711):318-28. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60883-7. Epub 2009 Aug 17
[PubMed PMID: 19692116]
[4]
Nuki G, Simkin PA. A concise history of gout and hyperuricemia and their treatment. Arthritis research & therapy. 2006:8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1
[PubMed PMID: 16820040]
[5]
Loeb JN. The influence of temperature on the solubility of monosodium urate. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1972 Mar-Apr:15(2):189-92
[PubMed PMID: 5027604]
[6]
Nian YL, You CG. Susceptibility genes of hyperuricemia and gout. Hereditas. 2022 Aug 4:159(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00243-y. Epub 2022 Aug 4
[PubMed PMID: 35922835]
[7]
Merriman TR, Choi HK, Dalbeth N. The genetic basis of gout. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 2014 May:40(2):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Feb 19
[PubMed PMID: 24703347]
[8]
Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM, American College of Physicians, American Physiological Society. Pathogenesis of gout. Annals of internal medicine. 2005 Oct 4:143(7):499-516
[PubMed PMID: 16204163]
[9]
Tan PK, Farrar JE, Gaucher EA, Miner JN. Coevolution of URAT1 and Uricase during Primate Evolution: Implications for Serum Urate Homeostasis and Gout. Molecular biology and evolution. 2016 Sep:33(9):2193-200. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw116. Epub 2016 Jun 26
[PubMed PMID: 27352852]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[10]
Abhishek A, Roddy E, Doherty M. Gout - a guide for the general and acute physicians. Clinical medicine (London, England). 2017 Feb:17(1):54-59. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-1-54. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28148582]
[11]
Scott JT. Asymptomatic hyperuricaemia. British medical journal (Clinical research ed.). 1987 Apr 18:294(6578):987-8
[PubMed PMID: 3119013]
[12]
Dalbeth N, Phipps-Green A, Frampton C, Neogi T, Taylor WJ, Merriman TR. Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident incident gout: an individual participant data analysis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2018 Jul:77(7):1048-1052. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212288. Epub 2018 Feb 20
[PubMed PMID: 29463518]
[13]
Wu EQ, Patel PA, Mody RR, Yu AP, Cahill KE, Tang J, Krishnan E. Frequency, risk, and cost of gout-related episodes among the elderly: does serum uric acid level matter? The Journal of rheumatology. 2009 May:36(5):1032-40. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.080487. Epub 2009 Apr 15
[PubMed PMID: 19369467]
[14]
Dalbeth N, So A. Hyperuricaemia and gout: state of the art and future perspectives. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2010 Oct:69(10):1738-43. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.136218. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20858623]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[15]
Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Willett W, Curhan G. Purine-rich foods, dairy and protein intake, and the risk of gout in men. The New England journal of medicine. 2004 Mar 11:350(11):1093-103
[PubMed PMID: 15014182]
[16]
Juraschek SP, Yokose C, McCormick N, Miller ER 3rd, Appel LJ, Choi HK. Effects of Dietary Patterns on Serum Urate: Results From a Randomized Trial of the Effects of Diet on Hypertension. Arthritis & rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.). 2021 Jun:73(6):1014-1020. doi: 10.1002/art.41614. Epub 2021 Apr 23
[PubMed PMID: 33615722]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[17]
Rai SK, Fung TT, Lu N, Keller SF, Curhan GC, Choi HK. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, Western diet, and risk of gout in men: prospective cohort study. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 2017 May 9:357():j1794. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1794. Epub 2017 May 9
[PubMed PMID: 28487277]
[18]
Huang HY, Appel LJ, Choi MJ, Gelber AC, Charleston J, Norkus EP, Miller ER 3rd. The effects of vitamin C supplementation on serum concentrations of uric acid: results of a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2005 Jun:52(6):1843-7
[PubMed PMID: 15934094]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[19]
Gao X, Curhan G, Forman JP, Ascherio A, Choi HK. Vitamin C intake and serum uric acid concentration in men. The Journal of rheumatology. 2008 Sep:35(9):1853-8
[PubMed PMID: 18464304]
[20]
Juraschek SP, Miller ER 3rd, Gelber AC. Effect of oral vitamin C supplementation on serum uric acid: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis care & research. 2011 Sep:63(9):1295-306. doi: 10.1002/acr.20519. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21671418]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[21]
Choi HK, Gao X, Curhan G. Vitamin C intake and the risk of gout in men: a prospective study. Archives of internal medicine. 2009 Mar 9:169(5):502-7. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.606. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 19273781]
[22]
Juraschek SP, Gaziano JM, Glynn RJ, Gomelskaya N, Bubes VY, Buring JE, Shmerling RH, Sesso HD. Effects of vitamin C supplementation on gout risk: results from the Physicians' Health Study II trial. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2022 Sep 2:116(3):812-819. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac140. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 35575611]
[23]
Jacob RA, Spinozzi GM, Simon VA, Kelley DS, Prior RL, Hess-Pierce B, Kader AA. Consumption of cherries lowers plasma urate in healthy women. The Journal of nutrition. 2003 Jun:133(6):1826-9
[PubMed PMID: 12771324]
[24]
Zhang Y, Neogi T, Chen C, Chaisson C, Hunter DJ, Choi HK. Cherry consumption and decreased risk of recurrent gout attacks. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2012 Dec:64(12):4004-11. doi: 10.1002/art.34677. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23023818]
[25]
Glynn RJ, Campion EW, Silbert JE. Trends in serum uric acid levels 1961--1980. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1983 Jan:26(1):87-93
[PubMed PMID: 6824508]
[26]
Takiue Y, Hosoyamada M, Kimura M, Saito H. The effect of female hormones upon urate transport systems in the mouse kidney. Nucleosides, nucleotides & nucleic acids. 2011 Feb:30(2):113-9. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2010.551645. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21360409]
[27]
Rho YH, Zhu Y, Choi HK. The epidemiology of uric acid and fructose. Seminars in nephrology. 2011 Sep:31(5):410-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.08.004. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 22000647]
[28]
Hak AE, Choi HK. Menopause, postmenopausal hormone use and serum uric acid levels in US women--the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis research & therapy. 2008:10(5):R116. doi: 10.1186/ar2519. Epub 2008 Sep 26
[PubMed PMID: 18822120]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[29]
Arromdee E, Michet CJ, Crowson CS, O'Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Epidemiology of gout: is the incidence rising? The Journal of rheumatology. 2002 Nov:29(11):2403-6
[PubMed PMID: 12415600]
[30]
Choi H. Epidemiology of crystal arthropathy. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 2006 May:32(2):255-73, v
[PubMed PMID: 16716879]
[31]
Ragab G, Elshahaly M, Bardin T. Gout: An old disease in new perspective - A review. Journal of advanced research. 2017 Sep:8(5):495-511. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 May 10
[PubMed PMID: 28748116]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[32]
Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG, Jordan JM, Katz JN, Kremers HM, Wolfe F, National Arthritis Data Workgroup. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2008 Jan:58(1):26-35. doi: 10.1002/art.23176. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18163497]
[33]
Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2011 Oct:63(10):3136-41. doi: 10.1002/art.30520. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21800283]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[34]
Kramer HM, Curhan G. The association between gout and nephrolithiasis: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III, 1988-1994. American journal of kidney diseases : the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 2002 Jul:40(1):37-42
[PubMed PMID: 12087559]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[35]
McCormick N, Lu N, Yokose C, Joshi AD, Sheehy S, Rosenberg L, Warner ET, Dalbeth N, Merriman TR, Saag KG, Zhang Y, Choi HK. Racial and Sex Disparities in Gout Prevalence Among US Adults. JAMA network open. 2022 Aug 1:5(8):e2226804. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.26804. Epub 2022 Aug 1
[PubMed PMID: 35969396]
[37]
Kuo CF, Grainge MJ, Mallen C, Zhang W, Doherty M. Rising burden of gout in the UK but continuing suboptimal management: a nationwide population study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2015 Apr:74(4):661-7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204463. Epub 2014 Jan 15
[PubMed PMID: 24431399]
[38]
Singh JA. Gout and comorbidity: a nominal group study of people with gout. Arthritis research & therapy. 2017 Sep 15:19(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1416-8. Epub 2017 Sep 15
[PubMed PMID: 28915838]
[39]
Bursill D, Taylor WJ, Terkeltaub R, Abhishek A, So AK, Vargas-Santos AB, Gaffo AL, Rosenthal A, Tausche AK, Reginato A, Manger B, Sciré C, Pineda C, van Durme C, Lin CT, Yin C, Albert DA, Biernat-Kaluza E, Roddy E, Pascual E, Becce F, Perez-Ruiz F, Sivera F, Lioté F, Schett G, Nuki G, Filippou G, McCarthy G, da Rocha Castelar Pinheiro G, Ea HK, Tupinambá HA, Yamanaka H, Choi HK, Mackay J, ODell JR, Vázquez Mellado J, Singh JA, Fitzgerald JD, Jacobsson LTH, Joosten L, Harrold LR, Stamp L, Andrés M, Gutierrez M, Kuwabara M, Dehlin M, Janssen M, Doherty M, Hershfield MS, Pillinger M, Edwards NL, Schlesinger N, Kumar N, Slot O, Ottaviani S, Richette P, MacMullan PA, Chapman PT, Lipsky PE, Robinson P, Khanna PP, Gancheva RN, Grainger R, Johnson RJ, Te Kampe R, Keenan RT, Tedeschi SK, Kim S, Choi SJ, Fields TR, Bardin T, Uhlig T, Jansen T, Merriman T, Pascart T, Neogi T, Klück V, Louthrenoo W, Dalbeth N. Gout, Hyperuricaemia and Crystal-Associated Disease Network (G-CAN) consensus statement regarding labels and definitions of disease states of gout. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2019 Nov:78(11):1592-1600. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215933. Epub 2019 Sep 9
[PubMed PMID: 31501138]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[40]
Bursill D, Taylor WJ, Terkeltaub R, Kuwabara M, Merriman TR, Grainger R, Pineda C, Louthrenoo W, Edwards NL, Andrés M, Vargas-Santos AB, Roddy E, Pascart T, Lin CT, Perez-Ruiz F, Tedeschi SK, Kim SC, Harrold LR, McCarthy G, Kumar N, Chapman PT, Tausche AK, Vazquez-Mellado J, Gutierrez M, da Rocha Castelar-Pinheiro G, Richette P, Pascual E, Fisher MC, Burgos-Vargas R, Robinson PC, Singh JA, Jansen TL, Saag KG, Slot O, Uhlig T, Solomon DH, Keenan RT, Scire CA, Biernat-Kaluza E, Dehlin M, Nuki G, Schlesinger N, Janssen M, Stamp LK, Sivera F, Reginato AM, Jacobsson L, Lioté F, Ea HK, Rosenthal A, Bardin T, Choi HK, Hershfield MS, Czegley C, Choi SJ, Dalbeth N. Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal-Associated Disease Network Consensus Statement Regarding Labels and Definitions for Disease Elements in Gout. Arthritis care & research. 2019 Mar:71(3):427-434. doi: 10.1002/acr.23607. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29799677]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[41]
Chhana A, Lee G, Dalbeth N. Factors influencing the crystallization of monosodium urate: a systematic literature review. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2015 Oct 14:16():296. doi: 10.1186/s12891-015-0762-4. Epub 2015 Oct 14
[PubMed PMID: 26467213]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[42]
So AK, Martinon F. Inflammation in gout: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nature reviews. Rheumatology. 2017 Nov:13(11):639-647. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.155. Epub 2017 Sep 28
[PubMed PMID: 28959043]
[43]
Chen J, Wu M, Yang J, Wang J, Qiao Y, Li X. The Immunological Basis in the Pathogenesis of Gout. Iranian journal of immunology : IJI. 2017 Jun:14(2):90-98
[PubMed PMID: 28630380]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[44]
Chhana A, Dalbeth N. Structural joint damage in gout. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 2014 May:40(2):291-309. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Feb 20
[PubMed PMID: 24703348]
[45]
Dalbeth N, Clark B, Gregory K, Gamble G, Sheehan T, Doyle A, McQueen FM. Mechanisms of bone erosion in gout: a quantitative analysis using plain radiography and computed tomography. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2009 Aug:68(8):1290-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.094201. Epub 2008 Aug 15
[PubMed PMID: 18708415]
[46]
Dalbeth N, Smith T, Nicolson B, Clark B, Callon K, Naot D, Haskard DO, McQueen FM, Reid IR, Cornish J. Enhanced osteoclastogenesis in patients with tophaceous gout: urate crystals promote osteoclast development through interactions with stromal cells. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2008 Jun:58(6):1854-65. doi: 10.1002/art.23488. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18512794]
[48]
Towiwat P, Chhana A, Dalbeth N. The anatomical pathology of gout: a systematic literature review. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2019 Apr 1:20(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2519-y. Epub 2019 Apr 1
[PubMed PMID: 30935368]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[49]
Hadler NM, Franck WA, Bress NM, Robinson DR. Acute polyarticular gout. The American journal of medicine. 1974 May:56(5):715-9
[PubMed PMID: 4825606]
[50]
Komarla A, Schumacher R, Merkel PA. Spinal gout presenting as acute low back pain. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2013 Oct:65(10):2660. doi: 10.1002/art.38069. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23818092]
[51]
Lumezanu E, Konatalapalli R, Weinstein A. Axial (spinal) gout. Current rheumatology reports. 2012 Apr:14(2):161-4. doi: 10.1007/s11926-012-0236-8. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 22318623]
[52]
Yü TF. Secondary gout associated with myeloproliferative diseases. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1965 Oct:8(5):765-71
[PubMed PMID: 5216775]
[53]
Lin HY, Rocher LL, McQuillan MA, Schmaltz S, Palella TD, Fox IH. Cyclosporine-induced hyperuricemia and gout. The New England journal of medicine. 1989 Aug 3:321(5):287-92
[PubMed PMID: 2664517]
[54]
Choi HK, Niu J, Neogi T, Chen CA, Chaisson C, Hunter D, Zhang Y. Nocturnal risk of gout attacks. Arthritis & rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.). 2015 Feb:67(2):555-62. doi: 10.1002/art.38917. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25504842]
[55]
Rakieh C, Conaghan PG. Diagnosis and treatment of gout in primary care. The Practitioner. 2011 Dec:255(1746):17-20, 2-3
[PubMed PMID: 22272526]
[56]
Shah D, Mohan G, Flueckiger P, Corrigan F, Conn D. Polyarticular Gout Flare Masquerading as Sepsis. The American journal of medicine. 2015 Jul:128(7):e11-2. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.12.025. Epub 2015 Jan 20
[PubMed PMID: 25614957]
[57]
Pascual E, Batlle-Gualda E, Martínez A, Rosas J, Vela P. Synovial fluid analysis for diagnosis of intercritical gout. Annals of internal medicine. 1999 Nov 16:131(10):756-9
[PubMed PMID: 10577299]
[58]
Sivera F, Andrés M, Quilis N. Gout: Diagnosis and treatment. Medicina clinica. 2017 Mar 22:148(6):271-276. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2016.10.019. Epub 2016 Dec 5
[PubMed PMID: 27931865]
[59]
Qaseem A,Harris RP,Forciea MA,Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians.,Denberg TD,Barry MJ,Boyd C,Chow RD,Humphrey LL,Kansagara D,Vijan S,Wilt TJ, Management of Acute and Recurrent Gout: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Annals of internal medicine. 2017 Jan 3
[PubMed PMID: 27802508]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[60]
Richette P,Doherty M,Pascual E,Barskova V,Becce F,Castañeda-Sanabria J,Coyfish M,Guillo S,Jansen TL,Janssens H,Lioté F,Mallen C,Nuki G,Perez-Ruiz F,Pimentao J,Punzi L,Pywell T,So A,Tausche AK,Uhlig T,Zavada J,Zhang W,Tubach F,Bardin T, 2016 updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2017 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 27457514]
[61]
FitzGerald JD, Dalbeth N, Mikuls T, Brignardello-Petersen R, Guyatt G, Abeles AM, Gelber AC, Harrold LR, Khanna D, King C, Levy G, Libbey C, Mount D, Pillinger MH, Rosenthal A, Singh JA, Sims JE, Smith BJ, Wenger NS, Bae SS, Danve A, Khanna PP, Kim SC, Lenert A, Poon S, Qasim A, Sehra ST, Sharma TSK, Toprover M, Turgunbaev M, Zeng L, Zhang MA, Turner AS, Neogi T. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis care & research. 2020 Jun:72(6):744-760. doi: 10.1002/acr.24180. Epub 2020 May 11
[PubMed PMID: 32391934]
[62]
Khanna D, Fitzgerald JD, Khanna PP, Bae S, Singh MK, Neogi T, Pillinger MH, Merill J, Lee S, Prakash S, Kaldas M, Gogia M, Perez-Ruiz F, Taylor W, Lioté F, Choi H, Singh JA, Dalbeth N, Kaplan S, Niyyar V, Jones D, Yarows SA, Roessler B, Kerr G, King C, Levy G, Furst DE, Edwards NL, Mandell B, Schumacher HR, Robbins M, Wenger N, Terkeltaub R, American College of Rheumatology. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 1: systematic nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapeutic approaches to hyperuricemia. Arthritis care & research. 2012 Oct:64(10):1431-46. doi: 10.1002/acr.21772. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23024028]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[63]
Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, Pascual E, Barskova V, Conaghan P, Gerster J, Jacobs J, Leeb B, Lioté F, McCarthy G, Netter P, Nuki G, Perez-Ruiz F, Pignone A, Pimentão J, Punzi L, Roddy E, Uhlig T, Zimmermann-Gòrska I, EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2006 Oct:65(10):1312-24
[PubMed PMID: 16707532]
[64]
Zhang W, Doherty M, Pascual E, Bardin T, Barskova V, Conaghan P, Gerster J, Jacobs J, Leeb B, Lioté F, McCarthy G, Netter P, Nuki G, Perez-Ruiz F, Pignone A, Pimentão J, Punzi L, Roddy E, Uhlig T, Zimmermann-Gòrska I, EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part I: Diagnosis. Report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2006 Oct:65(10):1301-11
[PubMed PMID: 16707533]
[65]
YU TF, GUTMAN AB. Study of the paradoxical effects of salicylate in low, intermediate and high dosage on the renal mechanisms for excretion of urate in man. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1959 Aug:38(8):1298-315
[PubMed PMID: 13673086]
[66]
YUE TF, DAYTON PG, GUTMAN AB. MUTUAL SUPPRESSION OF THE URICOSURIC EFFECTS OF SULFINPYRAZONE AND SALICYLATE: A STUDY IN INTERACTIONS BETWEEN DRUGS. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1963 Aug:42(8):1330-9
[PubMed PMID: 14060403]
[67]
Caspi D, Lubart E, Graff E, Habot B, Yaron M, Segal R. The effect of mini-dose aspirin on renal function and uric acid handling in elderly patients. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2000 Jan:43(1):103-8
[PubMed PMID: 10643705]
[68]
Segal R, Lubart E, Leibovitz A, Iaina A, Caspi D. Renal effects of low dose aspirin in elderly patients. The Israel Medical Association journal : IMAJ. 2006 Oct:8(10):679-82
[PubMed PMID: 17125112]
[69]
Zhang YK, Yang H, Zhang JY, Song LJ, Fan YC. Comparison of intramuscular compound betamethasone and oral diclofenac sodium in the treatment of acute attacks of gout. International journal of clinical practice. 2014 May:68(5):633-8. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12359. Epub 2014 Jan 29
[PubMed PMID: 24472084]
[70]
Alloway JA, Moriarty MJ, Hoogland YT, Nashel DJ. Comparison of triamcinolone acetonide with indomethacin in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis. The Journal of rheumatology. 1993 Jan:20(1):111-3
[PubMed PMID: 8441139]
[71]
Zeng L, Qasim A, Neogi T, Fitzgerald JD, Dalbeth N, Mikuls TR, Guyatt GH, Brignardello-Petersen R. Efficacy and Safety of Pharmacologic Interventions in Patients Experiencing a Gout Flare: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Arthritis care & research. 2021 May:73(5):755-764. doi: 10.1002/acr.24402. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 32741131]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[72]
Terkeltaub RA, Furst DE, Bennett K, Kook KA, Crockett RS, Davis MW. High versus low dosing of oral colchicine for early acute gout flare: Twenty-four-hour outcome of the first multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-comparison colchicine study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2010 Apr:62(4):1060-8. doi: 10.1002/art.27327. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20131255]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[73]
. Colchicine and other drugs for gout. The Medical letter on drugs and therapeutics. 2009 Nov 30:51(1326):93-4
[PubMed PMID: 20224523]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[74]
Todd BA, Billups SJ, Delate T, Canty KE, Kauffman AB, Rawlings JE, Wagner TM. Assessment of the association between colchicine therapy and serious adverse events. Pharmacotherapy. 2012 Nov:32(11):974-80. doi: 10.1002/phar.1125. Epub 2012 Sep 27
[PubMed PMID: 23019065]
[75]
Terkeltaub RA. Colchicine update: 2008. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism. 2009 Jun:38(6):411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.08.006. Epub 2008 Oct 29
[PubMed PMID: 18973929]
[76]
Khanna D,Khanna PP,Fitzgerald JD,Singh MK,Bae S,Neogi T,Pillinger MH,Merill J,Lee S,Prakash S,Kaldas M,Gogia M,Perez-Ruiz F,Taylor W,Lioté F,Choi H,Singh JA,Dalbeth N,Kaplan S,Niyyar V,Jones D,Yarows SA,Roessler B,Kerr G,King C,Levy G,Furst DE,Edwards NL,Mandell B,Schumacher HR,Robbins M,Wenger N,Terkeltaub R, 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 2: therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis care
[PubMed PMID: 23024029]
[77]
Sarawate CA, Patel PA, Schumacher HR, Yang W, Brewer KK, Bakst AW. Serum urate levels and gout flares: analysis from managed care data. Journal of clinical rheumatology : practical reports on rheumatic & musculoskeletal diseases. 2006 Apr:12(2):61-5
[PubMed PMID: 16601538]
[78]
Ragab AH, Gilkerson E, Myers M. The effect of 6-mercaptopurine and allopurinol on granulopoiesis. Cancer research. 1974 Sep:34(9):2246-9
[PubMed PMID: 4843532]
[79]
Weinberger A, Schindel B, Liberman UA, Pinkhas J, Sperling O. Calciuric effect of probenecid in gouty patients. Israel journal of medical sciences. 1983 Apr:19(4):377-9
[PubMed PMID: 6853140]
[80]
Keenan RT, Yeo AE, Lipsky PE. Pegloticase causes prolonged improvement in multiple disease parameters in patients with chronic refractory gout who maintain low serum urate levels. Clinical and experimental rheumatology. 2022 May:40(5):1006-1010. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3m095f. Epub 2022 Feb 25
[PubMed PMID: 35238750]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[81]
Zhang Y,Yang R,Dove A,Li X,Yang H,Li S,Wang J,Li WD,Zhao H,Xu W,Wang Y, Healthy lifestyle counteracts the risk effect of genetic factors on incident gout: a large population-based longitudinal study. BMC medicine. 2022 Apr 29
[PubMed PMID: 35484537]
[82]
Berman EL. Clues in the eye: ocular signs of metabolic and nutritional disorders. Geriatrics. 1995 Jul:50(7):34-6, 43-4
[PubMed PMID: 7601360]
[83]
Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Curhan G. Obesity, weight change, hypertension, diuretic use, and risk of gout in men: the health professionals follow-up study. Archives of internal medicine. 2005 Apr 11:165(7):742-8
[PubMed PMID: 15824292]
[83]
Elfishawi MM, Zleik N, Kvrgic Z, Michet CJ Jr, Crowson CS, Matteson EL, Bongartz T. The Rising Incidence of Gout and the Increasing Burden of Comorbidities: A Population-based Study over 20 Years. The Journal of rheumatology. 2018 Apr:45(4):574-579. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170806. Epub 2017 Dec 15
[PubMed PMID: 29247151]
[84]
Roubenoff R, Klag MJ, Mead LA, Liang KY, Seidler AJ, Hochberg MC. Incidence and risk factors for gout in white men. JAMA. 1991 Dec 4:266(21):3004-7
[PubMed PMID: 1820473]
[85]
Martinon F, Pétrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006 Mar 9:440(7081):237-41
[PubMed PMID: 16407889]
[86]
Krishnan E. Chronic kidney disease and the risk of incident gout among middle-aged men: a seven-year prospective observational study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2013 Dec:65(12):3271-8. doi: 10.1002/art.38171. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23982888]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[87]
Annemans L, Spaepen E, Gaskin M, Bonnemaire M, Malier V, Gilbert T, Nuki G. Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000-2005. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2008 Jul:67(7):960-6
[PubMed PMID: 17981913]
[88]
Kuo CF, Grainge MJ, Mallen C, Zhang W, Doherty M. Comorbidities in patients with gout prior to and following diagnosis: case-control study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2016 Jan:75(1):210-7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206410. Epub 2014 Nov 14
[PubMed PMID: 25398375]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[89]
Moon KW, Kim MJ, Choi IA, Shin K. Cardiovascular Risks in Korean Patients with Gout: Analysis Using a National Health Insurance Service Database. Journal of clinical medicine. 2022 Apr 11:11(8):. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082124. Epub 2022 Apr 11
[PubMed PMID: 35456221]
[90]
Cipolletta E, Tata LJ, Nakafero G, Avery AJ, Mamas MA, Abhishek A. Association Between Gout Flare and Subsequent Cardiovascular Events Among Patients With Gout. JAMA. 2022 Aug 2:328(5):440-450. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.11390. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 35916846]
[91]
Disveld IJM, Zoakman S, Jansen TLTA, Rongen GA, Kienhorst LBE, Janssens HJEM, Fransen J, Janssen M. Crystal-proven gout patients have an increased mortality due to cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases especially when having tophi and/or high serum uric acid levels: a prospective cohort study. Clinical rheumatology. 2019 May:38(5):1385-1391. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04520-6. Epub 2019 Mar 30
[PubMed PMID: 30929152]
[92]
Ioachimescu AG, Brennan DM, Hoar BM, Hazen SL, Hoogwerf BJ. Serum uric acid is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a preventive cardiology information system (PreCIS) database cohort study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2008 Feb:58(2):623-30. doi: 10.1002/art.23121. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18240236]
[93]
Vargas-Santos AB, Neogi T, da Rocha Castelar-Pinheiro G, Kapetanovic MC, Turkiewicz A. Cause-Specific Mortality in Gout: Novel Findings of Elevated Risk of Non-Cardiovascular-Related Deaths. Arthritis & rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.). 2019 Nov:71(11):1935-1942. doi: 10.1002/art.41008. Epub 2019 Sep 25
[PubMed PMID: 31169353]

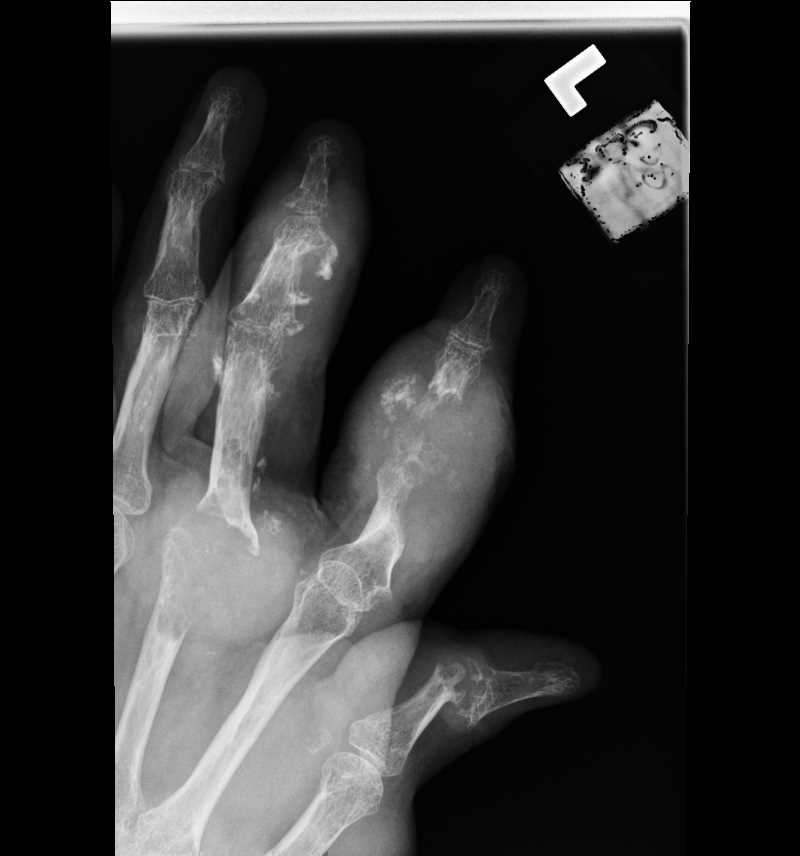
![Gout, [SATA]](/pictures/getimagecontent//6491)