Continuing Education Activity
Non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs (NMBDs) work by competing with acetylcholine (Ach) for binding sites on nicotinic alpha subunits. They produce skeletal muscle relaxation for endotracheal intubation, reduce patient movement to optimize operating conditions, and have been shown to improve compliance with mechanical ventilation. Since muscle relaxants lack analgesic or anesthetic properties, they should not be used without anxiolytic or hypnotic agents or in inadequately anesthetized patients due to increased risk of awareness during general anesthesia. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, methods of administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and toxicity of non-depolarizing, neuromuscular, blocking drugs, so providers can direct patient therapy to optimal outcomes in anesthesia and other conditions where non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs have therapeutic benefit.
Objectives:
- Describe the mechanism of action of non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs.
- Review the indications for using non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs.
- Summarize the potential adverse effects associated with non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs.
- Outline the importance of collaboration and communication among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes and treatment efficacy for patients who might benefit from non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs.
Indications
It is necessary to prevent spontaneous muscular contraction and movement when performing surgical procedures. The introduction of muscle relaxants has revolutionized the practice of anesthesia. By the end of the 1950s, non-depolarizing, neuromuscular blocking drugs (NMBDs), d-tubocurarine, and gallamine were available.[1] Although these two relaxants are no longer in use, several newer NMBDs have emerged with safer side effect profiles over the last 20 years.[2] Non-depolarizing muscle relaxants comprise the majority of clinically relevant neuromuscular blockers.[3] As their name indicates, they cause neuromuscular blockade without depolarizing the motor endplate.
Non-depolarizing NMBDs work by competing with acetylcholine (Ach) for binding sites on nicotinic alpha subunits, blocking Ach from binding to the receptor. In some instances, they can also cause direct blocking of the inotropic activity of Ach receptors.[3] They produce skeletal muscle relaxation for endotracheal intubation, reduce patient movement to optimize operating conditions, and research has shown them to improve compliance with mechanical ventilation. Notably, there has yet to be a non-depolarizing NMBD developed that can work faster than the rapid-onset, depolarizing muscle relaxant succinylcholine. However, onset can accelerate by using larger initial dosing of some non-depolarizing NMBDs, for example, rocuronium. Since muscle relaxants lack analgesic or anesthetic properties, they are not for use without anxiolytic or hypnotic agents or in inadequately anesthetized patients due to increased risk of awareness during general anesthesia.[4]
Mechanism of Action
The Ach receptor housed within the post-junctional motor neuron cell membrane is comprised of five glycoprotein subunits: two alpha subunits and one each of beta, gamma, and epsilon. The arrangement of these subunits is in a cylindrical fashion, with the center containing an ion channel. When Ach binds to the two alpha-subunits, there is ion flow through the central ion channel with subsequent depolarization of the motor neuron. A non-depolarizing NMBD is a quaternary ammonium compound with positively-charged nitrogen that imparts an affinity to nicotinic Ach receptors. It only needs to bind one of the two alpha subunits to block Ach, thus preventing depolarization and producing muscle relaxation.[5]
The two major structural classes of non-depolarizing agents include aminosteroid and benzylisoquinolinium. Recently, a third class has been developed, known as asymmetrical mixed-onium chlorofumarate (i.e., gantacurium).[6][7] Examples of common aminosteroids include atracurium, rocuronium, vecuronium, and pancuronium. Common benzylisoquinolinium compounds include atracurium, cisatracurium, and mivacurium.[2]
It remains unknown how the various drugs' structures affect their onset of action, and this onset time appears to have an inverse relationship with drug potency.[8]
Administration
Weight-based dosing scalars are important because administration based on total body weight may result in overdose, while dosing based on ideal body weight may be sub-therapeutic. Recommendations are that non-depolarizing NMBDs are dosed based on ideal body weight to avoid prolonged paralysis.[9] Intravenous (IV) injection is the most common mode of delivery, although intramuscular (IM) injections may be possible for some non-depolarizing relaxants. The 95% effective dose (ED95) for NMBDs specifies the dose that produces 95% twitch depression in 50% of individuals. One to two times the ED95 dose for a particular non-depolarizing NMBD is the typical dose administered for intubation.[10][11]
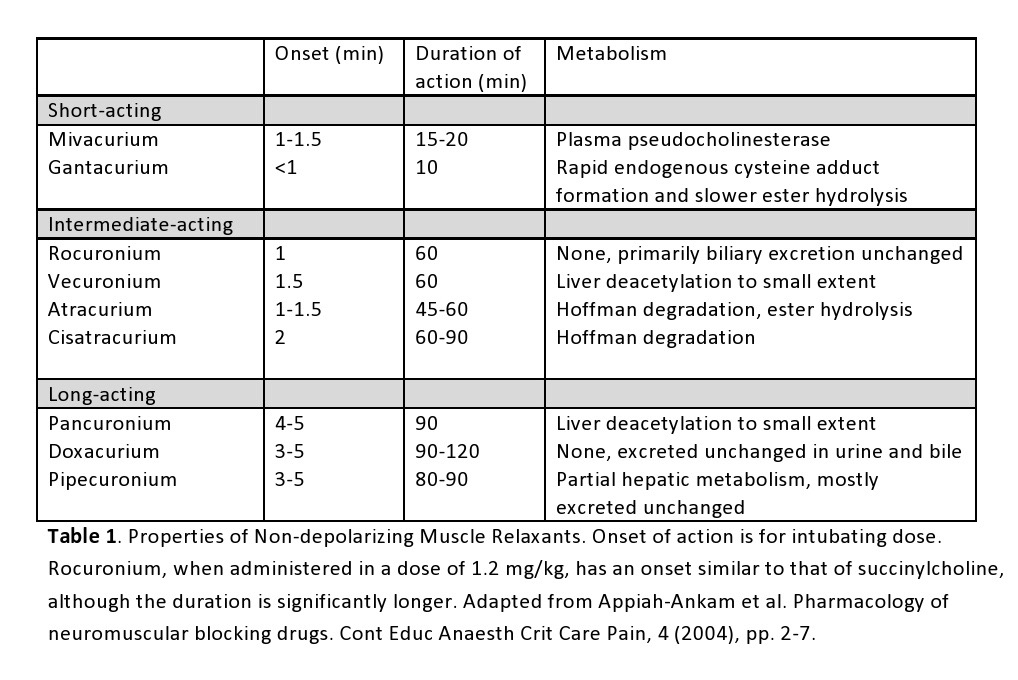
A provider’s choice of non-depolarizing NMBD depends on the desired speed of onset, duration of action, route of elimination, and side effects. For instance, muscle relaxants with a rapid onset (i.e., rocuronium) and brief duration may be desirable when endotracheal intubation is the reason for paralysis. On the other hand, a longer-acting agent like pancuronium may also produce intubating conditions in 90 seconds, but at the cost of pronounced tachycardia within the patient and a block that may be irreversible by an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (for over 60 minutes), increasing the risk of postoperative pulmonary complications.[12] The table below displays the characteristics of various non-depolarizing NMBDs.[10][11]
Duration of action for some of the most commonly used agents:
- Atracurium - 30 minutes or less
- Rocuronium - 45 to 70 minutes
- Pancuronium - 180 minutes or longer
- Vecuronium - 30 to 40 minutes
Adverse Effects
A non-immunologic histamine release occurs with the administration of benzylisoquinolinium compounds, typically mivacurium, atracurium, and doxacurium. This reaction is dose-related and affected by delivery rate, leading to positive chronotropy (H receptors), positive inotropy (H receptors), positive dromotropy (H receptors), skin flushing, and hypotension from peripheral vasodilation, and rarely bronchospasm. In fact, the non-depolarizing paralytic drug rapacuronium was withdrawn from the market as a result of its bronchospasm risk.[13]
Several large-scale studies showed that NMBDs are the most common causative agents of anesthesia-related anaphylaxis.[14][15] A prior history for anaphylaxis to one non-depolarizing NMBD also places a patient at an increased risk of cross-reactivity to another non-depolarizing NMBD.
Other notable side effects are drug-specific. Pancuronium may cause tachycardia and hypertension due to its vagolytic mechanism on nodal cells mediated through muscarinic receptors. Laudanosine, a metabolite of atracurium and cis-atracurium, may accumulate and cause central nervous system stimulation with resultant seizures. Finally, in critically ill patients, long-term infusions of non-depolarizing NMBDs, particularly aminosteroids, can lead to profound weakness, termed critical illness polymyoneuropathy (CIP).[16]
Drug interactions may potentiate weakness from non-depolarizing muscle relaxants, including volatile anesthetics, local anesthetics, certain antibiotics (i.e., aminoglycosides), and magnesium. Physiological alterations may also potentiate paralysis, including respiratory acidosis, metabolic alkalosis, hypothermia, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, and hypermagnesemia.[12][17][18]
Contraindications
Prior hypersensitivity reactions and inadequate sedation are contraindications. The provider should also consider the metabolism of certain non-depolarizing NMBDs. Only pancuronium and vecuronium are metabolized to any significant degree by the liver (deacetylation), and thus caution is advised in hepatic failure. Vecuronium and rocuronium undergo biliary excretion and may accumulate to toxic levels in extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Relaxants that primarily undergo renal excretion (e.g., doxacurium, pancuronium, pipecuronium) should be avoided in renal failure. Atracurium and cisatracurium are unique NMBDs because they undergo spontaneous degradation via Hofmann elimination. The metabolism of mivacurium is via plasma pseudocholinesterase, similar to succinylcholine.[10]
Monitoring
Patients who have received NMBDs require continuous pulse oximetry, cardiac monitoring, and end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. Peripheral nerve stimulation works to measure the depth of neuromuscular blockade. Typically, the ulnar and facial nerves are stimulated for monitoring. Neuromuscular blockade generally occurs more rapidly in laryngeal adductors, diaphragm, and masseter than in the adductor pollicis. Utilizing the nerve stimulator, the train of four (TOF) commonly helps assess blockade. It consists of four stimuli delivered at a frequency of 2 Hertz, and the ratio of the amplitude between the fourth to the first twitch response estimates the degree of the block. About 75% of Ach receptors become antagonized when the fourth twitch from TOF disappears, 85% receptor occupancy occurs when the third twitch disappears, 90% receptor occupancy occurs when the second twitch disappears, and 95% to 100% receptor occupancy occurs when the first twitch disappears. Adequate relaxation for surgery is present when 1 to 2 twitches of the TOF are present.[19]
Other unique observations noted on the peripheral nerve stimulator when a non-depolarizing NMBD paralyzes a patient include a tetanic fade response, post-tetanic potentiation, potentiation of blockade by other non-depolarizing NMBDs, and antagonism of the block by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Since TOF is user-dependent and introduces a considerable margin of error, other modalities are also available, including acceleromyography, strain-gauge monitoring, and electromyography.[20][21]
After the reversal of neuromuscular blockade, a thorough evaluation of muscle strength is necessary. A TOF ratio of 0.9 is the usual recommendation, although the visual estimation of the TOF may not be accurate. A sustained tetanic response, the ability to lift one’s head for 5 to 10 seconds, and good grip strength also suggest an adequate recovery.[22]
Toxicity
Higher than recommended dosing, for example, based on total body weight, may cause prolonged paralysis beyond the time required for surgery; this may manifest with generalized weakness, decreased respiratory reserve, and even apnea.[23] The management of toxicity should focus on airway maintenance and respiratory support to maintain oxygenation until the NMBD undergoes metabolism. As mentioned, non-immunologic histamine release is dose-dependent and may lead to significant hypotension and possibly bronchospasm if utilizing toxic doses.
Reversal of the NMBD can be done with anticholinesterase medications such as neostigmine or edrophonium. These anticholinesterase medications must be accompanied by an anticholinergic drug such as glycopyrrolate or atropine to block the ACH activity at the muscarinic receptors. Rocuronium and vecuronium specifically can be reversed with sugammadex, a selective relaxant binding agent (SRBA), offering a more rapid onset of reversal than neostigmine and without the muscarinic side effects. However, sugammadex may interfere with the efficacy of oral contraceptives, and an alternative form of contraception is recommended for the week following administration.[24]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
All interprofessional healthcare team members, including the nurse anesthetist, anesthesiologist, emergency medicine physician, and critical care specialist, who use neuromuscular blockers, must closely monitor all patients. These agents are usually administered to intubated patients, and hence, airway maintenance and respiratory support are vital. Muscle strength should undergo a regular assessment to determine if the drug's action has diminished. Pharmacists should also verify the agents and dosing when ordered outside the operating room and ensure no potential drug interactions exist with the patient's current medication profile. It is prudent to assign one individual whose sole responsibility is monitoring the patient's vitals and other signs associated with NMBD use. This would be the anesthesia provider inside the operating room. Any issues need to be reported to the surgeon or anesthesiologist immediately. Only through this type of collaborative care can the interprofessional healthcare team ensure that these agents are used safely and appropriately to direct patient outcomes optimally. [Level 5]